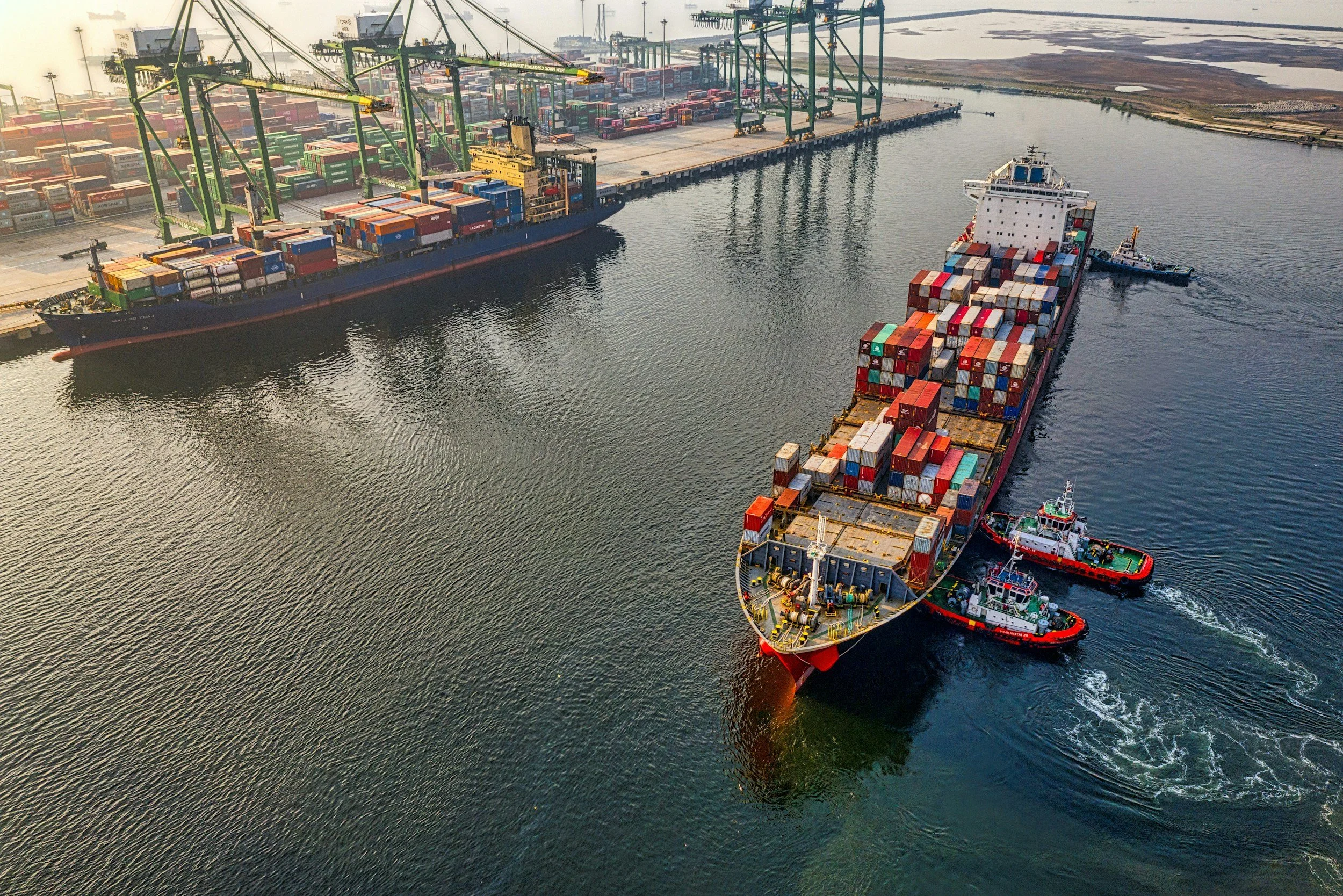
Decarbonization of Shipping
FUTURE SCENARIO
The shipping industry rapidly decarbonizes as regulatory mandates, carbon pricing, and technological advancements reshape maritime logistics. The International Maritime Organization (IMO) enforces zero-emission fuel requirements, while green corridors—designated clean shipping routes—accelerate sustainable freight transport.
Hydrogen and ammonia-powered vessels replace fossil fuels, with ports upgrading refueling and electrification infrastructure. AI-driven route optimization reduces emissions, and wind-assisted propulsion reemerges to enhance efficiency. Large-scale ship recycling integrates circular economy principles, ensuring sustainable fleet management. Autonomous and remotely operated vessels improve logistics, optimizing energy use.
With these changes, shipping transforms into a leader in green logistics. The industry’s shift fuels advancements in alternative energy, accelerating hydrogen and biofuel adoption across sectors. Maritime hubs integrate sustainable shipbuilding and zero-emission transport, making shipping a key driver of global decarbonization. Once a major polluter, the industry now stands at the forefront of sustainable trade, proving that policy enforcement and technological innovation drive systemic change.
Supporting Trends
-
Marine Workforces
SOCIAL
There's an increasing focus on marine workforce development and new skills for a workforce that can work in evolving areas of the ocean economy.
-
Blue Credits and Carbon
ECONOMIC
The development of ocean credit markets incentivizes sequestration projects in marine environments, contributing to restoration.
-
Alternate Fuels for Ships
ECONOMIC
Alternate fuels such as hydrogen and ammonia, and hybrid biofuels are gaining momentum along with retrofit engines and sails for net-zero goals.
-
Integrated Ocean Management
ECONOMIC
Collaborative platforms, marketplaces and applications facilitate exchange of goods and services, allowing parties to share value.
Barriers
-
Slow industry-wide adoption due to high retrofitting costs.
-
Lack of global regulatory alignment on shipping emissions policies.
-
Technological readiness gaps for scalable green fuel adoption.
Opportunties
-
Hydrogen and ammonia-based fuels reducing maritime carbon footprints.
-
AI-driven route optimization reducing fuel consumption.
-
Circular economy models integrating recycled shipbuilding materials.
Potential Roadmap
-
Green Corridors and Carbon Pricing
2025
Major trade routes implement green shipping corridors, with incentives for zero-emission vessels and penalties for high-emission operations.
-
Hydrogen Fuel Infrastructure
2030
Port facilities upgrade to support hydrogen, ammonia, and electrification, accelerating large fleet transitions to alternative fuels.
-
Autonomous Technology Logistics
2035
Autonomous and AI-driven vessel management reduces emissions through optimized routing, handling, predictive maintenance, port efficiency.
-
Circular Economy in Shipbuilding
2040
Recycling and sustainable ship manufacturing replace outdated vessel disposal practices, reducing industry waste.
-
Industry-wide Decarbonization
2050
Zero-emission fuels and closed-loop supply chains make shipping a net-zero industry, reshaping global trade logistics.
-
Scenarios
Collectively imagining what the future of the oceans might looks like in different contexts.
-
Drivers
Macro-level drivers that create broad-reaching impact, and influence our present and future.
-

Trends
Emerging trends are specific areas of change that hold potential for significant impact.

Let’s Work Together
Join our ocean-tech network.


