Renewable Energy
In 2023, the global capacity of marine energy reached 527 megawatts; derived from the kinetic energy of ocean waves, tides, salinity, and thermal differences.
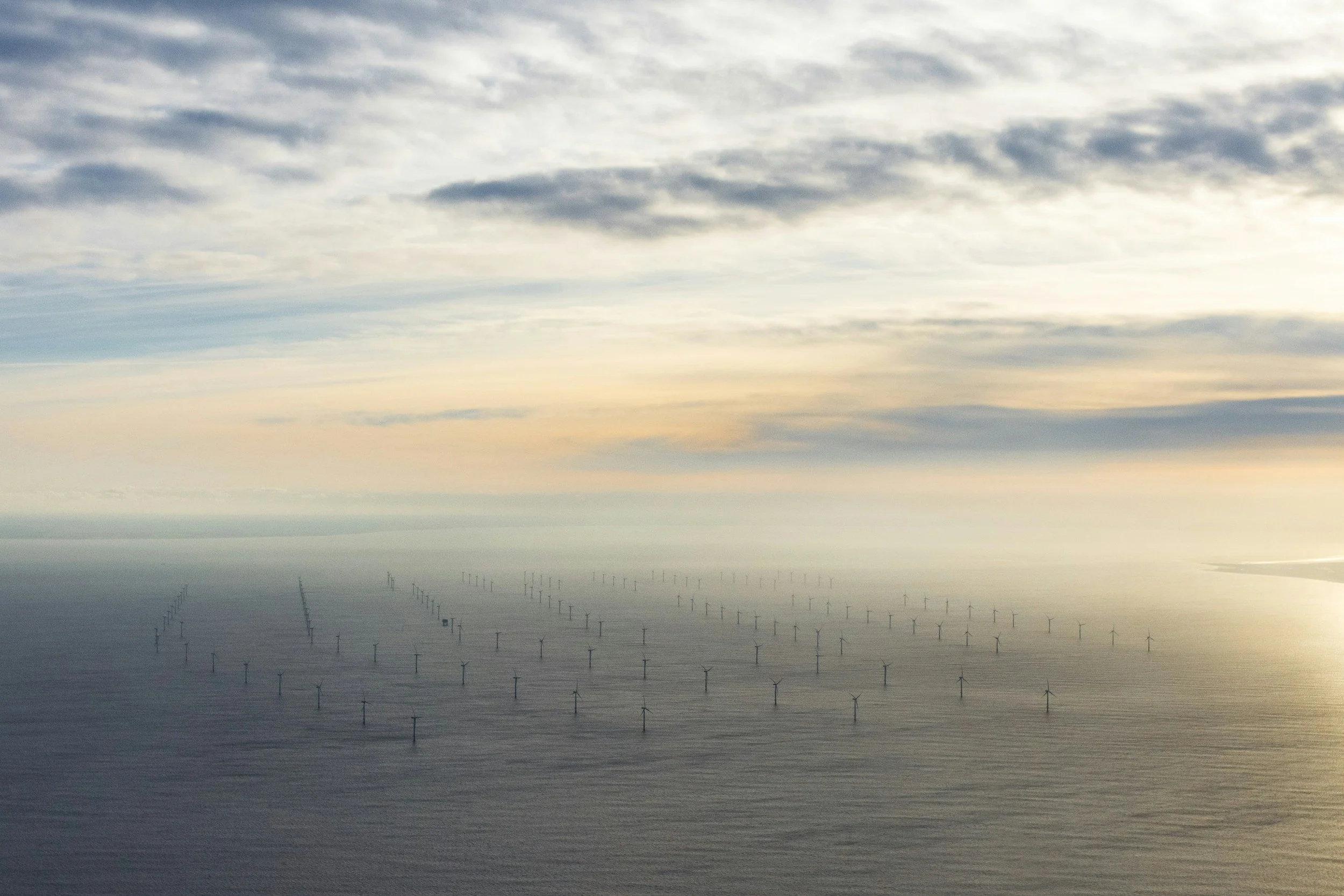
A total of 64.3 GW of global offshore wind capacity across three continents and 19 countries was in operation by the end of 2022, accounting for 7.1% of global wind power installation. Offshore wind, wave, tidal and geothermal energy are being expanded, and need to consider the design and strategic placement to minimize impacts and maximize outputs. Developing sustainable and resilient approaches to power technologies need to address the issues of cost, environmental impact, and regulations while reducing the time, cost and risks of getting projects built.
Although federal tax credits for wind and solar have played an important role in the clean energy revolution, it has largely been driven by state policies and market forces, as innovators, investors, consumers and forward-thinkers embrace the future. This means taking advantage of the enormous potential of offshore wind and new opportunities for green hydrogen manufacturing as well as wave, tidal-stream and ocean thermal energy conversion (OTEC) energy generation. The scaled potential of many of these technologies still need reliable long-term data, particularly in regard to how they affect marine ecosystems and coastal communities.
Regional Emergence of Clean Energy
In 2016, five diesel generators that powered Block Island in Rhode Island, were replaced by five offshore wind turbines – America’s starting five, at a30 MW capacity which now power 17,000 homes with and provide 2.5% of the state’s net generation. The Revolution Wind Project (704 MW) also presents economic and environmental opportunities, which will supply 400 MW of electricity to Rhode Island and 304 MW to Connecticut.
Massachusetts leads in offshore wind energy initiatives in New England with the Vineyard Wind project, which upon completion, aims to provide 800 MW of power—enough to supply over 400,000 homes. This project is part of a broader state plan to develop an additional 1600 MW of offshore wind energy by 2027. Maine is notably focusing on tidal energy with the deployment of tidal turbines in the Bay of Fundy. This project is still in the early stages but represents a significant potential for renewable energy.
Connecticut launched a statewide initiative Energy Storage Solutions program (1000 MW), a joint effort between the Connecticut Green Bank and utilities like Eversource to improve grid reliability through energy storage for resilience in vulnerable coastal communities.
Key Attributes
-
Offshore Wind
Turbines installed at sea harness strong, consistent winds to generate clean electricity. Floating and fixed platforms can power millions while minimizing land use.
-
Wave Energy
Devices capture the kinetic energy of surface waves to produce electricity. Still emerging, wave power offers a predictable and vast renewable resource.
-
Tidal Energy
Uses the rise and fall of tides or underwater currents to drive turbines. Reliable and site-specific, tidal power is ideal for coastal and estuarine areas.
-
Ocean Thermal Energy
Converts temperature differences between warm surface water and cold deep water into power. Best suited for tropical regions, it offers continuous, base-load electricity potential.
-
Energy Storage
Essential for balancing variable marine energy with grid demand and stability. Includes batteries, pumped storage, and new tech integrated with offshore platforms.
-
Biofuels and Hydrogen
Derived from algae or seawater electrolysis, offering transportable clean fuel. They can power ships and coastal industries while supporting a circular, low-carbon economy.
-
Geothermal
Taps heat from the Earth’s crust near mid-ocean ridges or volcanic zones. A niche but promising source for local, decentralized clean energy in tectonically active regions.
-
Scenarios
Collectively imagining what the future of the oceans might looks like in different contexts.
-
Drivers
Macro-level drivers that create broad-reaching impact, and influence our present and future.
-

Trends
Emerging trends are specific areas of change that hold potential for significant impact.

Let’s Work Together
Join our ocean-tech network.



